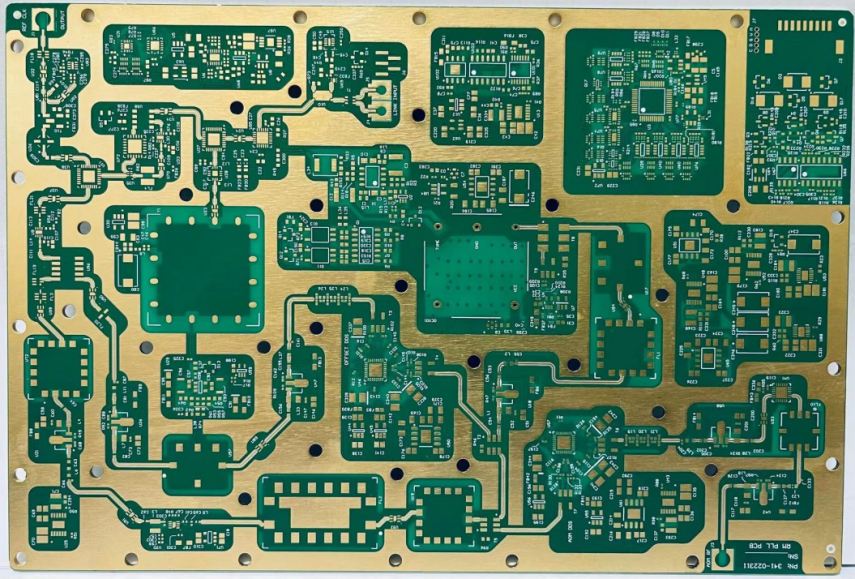
High Frequency PCB
What is High-Frequency PCB?
A high-frequency PCB refers to a special PCB that has a frequency range of 500MHz to 2GHz. This is a very high-frequency range that is not achievable in standard PCBs, which is why these PCBs are used for particular purposes where high-frequency signals are transmitted. High-frequency PCB is a circuit board produced on microwave substrate copper clad board using part of ordinary rigid circuit board manufacturing methods or using unique processing methods. Due to high frequency, communication and signal transmission are carried out at a faster rate. High-frequency PCBs’ primary use is in wireless communications, including satellites, telecommunication, and radar systems.
Why High-Frequency PCB?
When it comes to transmitting a signal at a higher frequency, there are many chances of losses, delays, and distortion in the signal. Thus, if we use a standard PCB for high-speed or high-frequency purposes, the results will not be optimum. The signals might get lost, or there could be huge losses after receiving the signal.
Furthermore, we cannot eliminate the use of high-frequency signals in the circuit because it’s the future. Nowadays, wireless transmission is widespread, and the best example is a Wi-Fi router working at your home. Some complex components and switches need signals faster, so the signal has a higher frequency. In simple words, high-frequency applications are increasing day by day because of the advantages that it offers. Thus, there is no choice to go for low-frequency signals to avoid the problem.
The only solution to these problems is the high-frequency PCB. A high-frequency is made of unique materials and has some specific features that allow it to transfer high-frequency signals with minimal loss. The High-frequency PCB is ideal for high-speed applications.
Materials for High-Frequency PCB
The materials that are used for high-frequency PCBs have unique qualities. If the material you have chosen is correct, it will offer the optimum results. Before you select any material, you need to go through some specifications to know whether the material is suitable for the application or not.
The important factors that you need to look at are,
Dielectric Constant(DK)
Dissipation Factor(DF)
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
Moisture Absorption
Some Common High-Frequency PCB Materials
By considering the above factors, some common materials that are used for high-frequency PCBs. Some of them are:
High Performing FR-4
PTFE
Ceramic-filled PTFE
Ceramic-fille Hydrocarbon
E-fibre glass
Teflon is one of the best and most widely used materials for high-frequency PCBs. It can offer stable and optimum results. But it is more expensive as compared to FR-There are some popular and trusted manufacturers of high-frequency PCB materials; some of them are:
Rogers (RO03001, RO03003, RO3010, RO4350B, RO4450B, RO4350 HF, RO4003)
Isola IS620 E-fibre glass
Isola FR408, FR 408 HR
Isola IS 415
Arlon 85N
Taconic RF-35 Ceramic
Taconic TLX
GIL Taconic
Nelco N4000-12/N4000-12SI
Nelco N4000-13EP/N4000-13EPSI
Nelco N8000
Hitachi LX-67Y, FX II
Getek
Panasonic Megtron +
Panasonic R2125
Panasonic Megtron VI
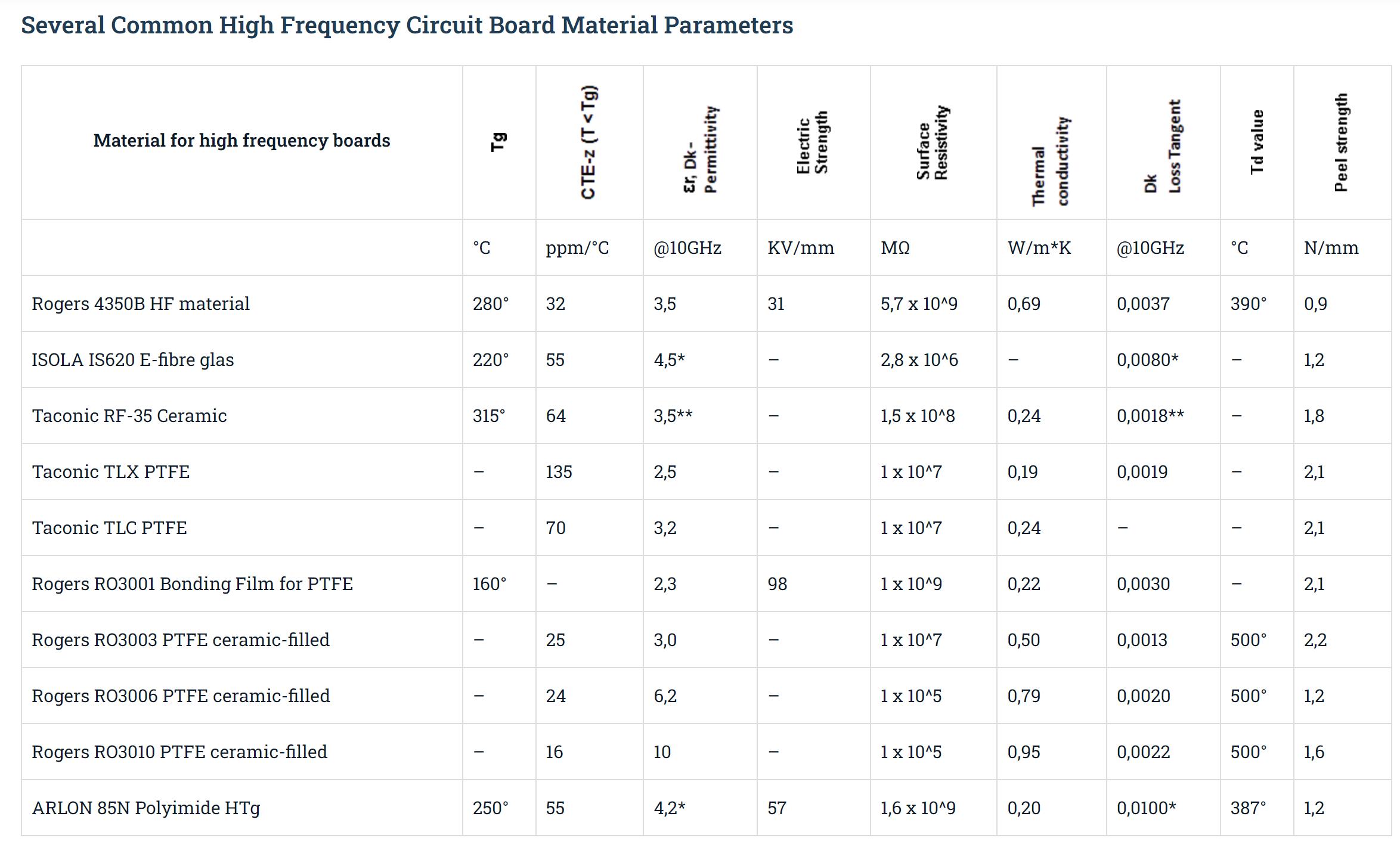
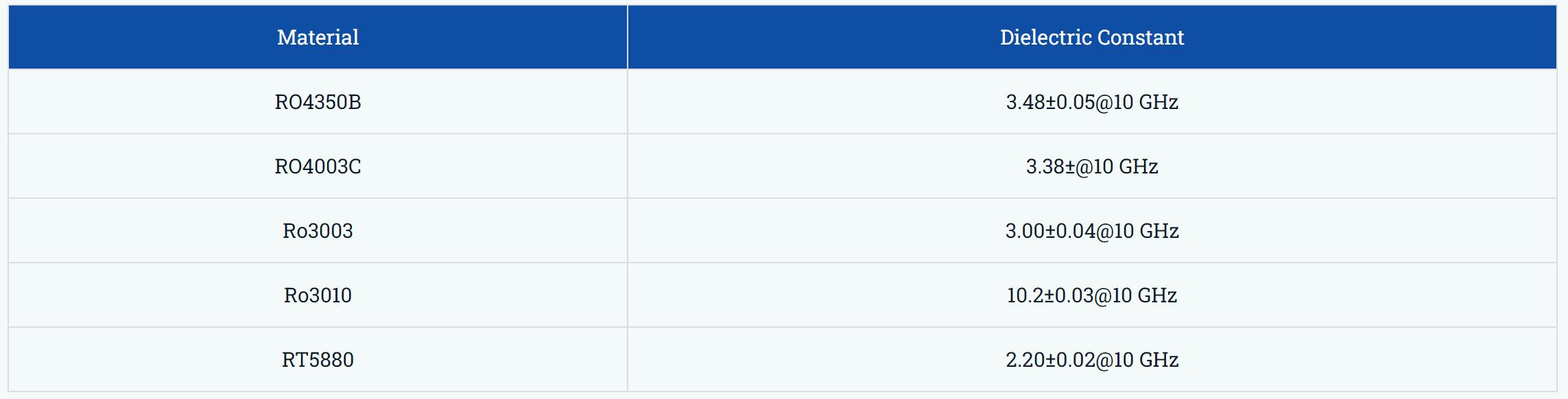
We manufacture high-frequency PCBs with frequencies typically in the range from 500MHz to 2GHz. The following table shows some of our common-use materials for High-Frequency PCBs manufacturing.
Factors Influencing A High Frequency PCB Design
Some of the factors needed to design high frequency PCB are mentioned below:
The selection of PCB material for high-speed digital circuits is influenced by several factors. The high frequency PCB must offer following features apart from a good structural build-up. Impedance controlled multilayers
Sandwich buildup for material combinations
Controlled production line
Signal loss tolerance
Heat sinking ability
Operating temperature(temperature expansion, stability over a temperature range)
Production cost

 Chinese
Chinese English
English Russian
Russian Spanish
Spanish Portuguese
Portuguese